Theme: Advancing the Future of Healthy Aging
Aging Meet 2019
Join us for the AGING MEET 2019
ME Conferences takes a lot of privilege to welcome all the scholars and researchers from all around the world to expatiate about their respective scientific research at “Aging, Health, Wellness Conference: For a better Aging Care” which is CPD accredited. An opportunity to experience this grand colloquium along with the most alluring city Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia on April 22-23, 2019
Aging Meet 2019 is a global event focusing on the core knowledge and major advances in the ever-expanding field of Aging and Geriatric Medicine by attracting experts on a worldwide scale. It is an international platform to discuss the innovative researches and developments in the Aging and Geriatric Medicine. It will be a brilliant opportunity to meet prominent personalities and to learn the most recent technological progressions.
Why to Attend Aging Conference?
Aging Meet 2019 aims to bring together leading academic scientists, researchers and research scholars to exchange and share their experiences and research results about all aspects of Aging and Geriatric Medicine. It also provides the premier interdisciplinary forum for researchers, practitioners and educators to present and discuss the most recent innovations, trends, and concerns, practical challenges encountered and the solutions adopted in the field of Aging and Geriatric Medicine. The Ultimate goal of the conference is to help the medical professionals in the geriatric field as well as general public to understand, empathize and take prompt actions to help old people across the globe.
Who Attends?
-
Geriatricians
-
Physicians
-
Geriatric Physicians
-
Medical Directors
-
Dental Professionals
-
Geriatric Doctors
-
Ophthalmologists
-
Rheumatologists
-
Clinical Geriatrics
-
Cardiologists
-
Geriatric Nurses
-
Pulmonologists
-
Pharmacists
-
Geriatric Specialist
-
Occupational Therapists
-
Healthcare Faculty
-
Social Workers
-
Community care coordinators
-
Palliative care specialists
-
Business delegates and industry professionals
-
Researchers
-
Students and others interested in the field of Geriatrics
Track 1: Aesthetic Medicine
Aesthetic medicine is an inclusive term for specialities that concentrate on enhancing cosmetic appearance thru the treatment of conditions which includes scars, skin laxity, wrinkles, moles, liver spots, excess fat, cellulite, unwanted hair, skin discolouration, and spider veins. Aesthetic medicine incorporates both surgical and non-surgical procedures. Traditionally, aesthetic medication incorporates dermatology, reconstructive surgery and plastic surgery. Aesthetic medicine speciality isn't always constrained to dermatologists and plastic surgeons as doctors of all specialities seek to offer services to deal with their patient's aesthetic needs and desires
-
Aging science
-
Cosmeceuticals
-
Cosmetic and Plastic surgery
-
Dermatology
-
Non-invasive procedures
-
Physical surgery
-
Reconstructive surgery
Track 2: Aging and Gerontology
Aging is the process of becoming older. Aging can also be referred to as single cells within an organism which have ceased dividing (cell senescence) or to the population of a species (population aging). It represents the accumulation of modifications in an individual over time, encompassing physical, mental, and social modifications.
Gerontology is a multidisciplinary study that includes biology, psychology and sociology. It is the study of the social, cultural, mental, cognitive, and biological factors of aging.
-
Biogerontology
-
Environmental gerontology
-
Jurisprudential gerontology
-
Psychogerontology
-
Sociogerontology
Track 3: Aging and Mental Health
Aging involves a change in lifestyle for most people and it's important to take care of mental health as well as physical health. There's an assumption that mental health problems are a 'normal' aspect of aging but older people don't develop mental health problems, and they can be helped if they do. Most have good mental health; many older adults are at risk of developing mental disorders, neurological disorders or substance use problems as well as other health conditions such as diabetes, hearing loss, and osteoarthritis.
Mental health among older adults is a multifaceted concept that reflects a range of clinical research activity, rather than a unified theoretical entity.
-
Alcoholism and Addiction
-
Dementia
-
Depression
-
Loneliness
-
Medication
-
Neuroplasticity
Track 4: Aging and Technology
Technology plays a vital role in the welfare of elderly people like it improves the education and training in online technologies for elder adults and gains them access through online services. It helps the adults in treating with disasters and emergency situations. Due to the advancement in technology, we could see the advancement of telehealth innovations. It helps and supports in designing better products for the needs of elderly people.
-
Activity sensors and Behavioral diagnostics
-
Biosensors and Bodily diagnostics
-
Health-related technology
-
Nanotechnology
-
Personal health informatics
-
Social engagement
-
Stem cell technology
-
Telemedicine\telehealth
Track 5: Aging Care Management
Geriatric Management or Aging Care Management is the process of planning and coordinating the elderly people or the one with physical or mental impairments to improve their quality of life or meet their long-term requirements. Geriatric professionals have knowledge over psychology, family dynamics, public and other private resources to support elderly people. Geriatric care management generally includes healthcare management and the psychological care accompanying all the other kinds of needs such as housing, home care services and also any social and legal issues.
-
Aging care service
-
Assessment and Monitoring
-
Education and advocacy
-
Geriatric Care Manager
-
Planning and Problem-solving
-
Socialization and entertainment
Track 6: Aging Disorders
It is most often found that the frequency of the diseases associated with aging is found to increase rapidly in relation to the process of senescence. Some of the diseases associated with aging include Alzheimer’s disease, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cataracts and arthritis. Aging generally increases the effectivity of these diseases whereas the genetics decides the occurrence of these diseases. Understanding the biology of senescence is very much important in understanding the age-related diseases. Greying of hair is also one of the important changes associated with aging.
-
Chronic diseases
-
Disorders of Accelerated Aging
-
Neurological disorder
-
Premature aging disorders
Track 7: Anti-Aging Strategies
There is a fact saying that if you are too skinny, you will appear older enough and if you are too heavy you will age more quickly. So the maintenance of anti-aging strategies becomes very important. The main anti-aging strategy includes eating/diet, stress reduction, regular physical and age-appropriate tests and consistent exercise and sufficient sleep. One should know that beginning the anti-aging strategies at the early stage is more beneficial. The goal of anti-aging strategies is to replace the hormones that will naturally cause aging through hormone replacement therapy. HRT promotes a better standard of living.
-
Anti-aging supplements
-
Cosmetological care
-
Dietary changes
-
Moderate aerobic exercise
-
Stress management
Track 8: Antioxidants and Aging
Antioxidants are generally referred to as the molecules that reduce the probability of aging by neglecting or standardizing the level of oxidants with or without free radical activity. The so-called anti-oxidants molecules can be supplied through the dietary supplements or can be used as the constituents in cosmetics for the skin and they act as the key to long-lasting youth. The life span and the process of aging are interrelated in such a way that throughout the lifespan the aging process should be maintained slowly. The latest research has been carried out to treat the skin wrinkles with the nano-antioxidant formulations.
-
Aging research
-
Anti-Aging
-
Antioxidant supplementation and clinical conditions
-
Free radical theory
-
Longevity Determinant Genes (LDGs)
-
Oxidative damage
-
Slow aging process
Track 9: Cultural Diversity in Aging
Cultural diversity plays an important role in aging. Culture describes a group whose individuals share common convictions, values, traditions, symbols, dialect, and socialization styles. As a person moves through the stages of life, he or she encounters an assortment of cultures through membership in families, occupations, communities, and services. Each culture contributes to the unique composition of a given person. Aging populations are getting to be more different in terms of colour, culture, character, inability, and socio-economic standing. As a result, the requirement for socially competent experts and businesses that serve and give products to older adults is progressively important.
-
Aging demographics
-
Age-related cognition
-
Cultural psychology
-
Cultural values
-
Social relationship
-
Socioemotional selectivity theory
Track 10: Economic and Social Impact of Aging
The challenge of global population aging has been brought into sharper awareness. A number of nations are consequently reconsidering their pension and health care provisions, which account for as much as 40% of all government spending in superior economies. But population aging is an international phenomenon so that it will continue to have an effect on all areas of the world. By 2050 there might be the same number of old as young in the international, with 2 billion people aged 60 or over and every other 2 billion below age 15, each group accounting for 21% of the world’s population.
-
Economic and Social Consequences
-
Care work
-
Fertility, Mortality and Life Expectancy
-
Population aging
-
Social security
Track 11: Evolution of Aging
Why do we age? This issue remains a major puzzle of science. Evolution is the process whereby genetic codes are adjusted, at first as the result of “transmission error.” Evolution is subsequently highly dependent on the details of the genetic communications and data storage scheme including the computerized benefits and confinements. In addition to clarifying why aging happens, the evolutionary hypothesis moreover gives knowledge into the mechanisms underlying the complex cellular and molecular changes that contribute to senescence, as well as an array of testable forecasts
-
Antagonistic pleiotropy
-
Classical aging theories
-
Disposable soma theory
-
Mutation accumulation
-
Phenoptosis
-
Programmed aging theories
Track 12: Frailty/Sarcopenia
Frailty is a common negative consequence of aging. Sarcopenia is the syndrome of loss of muscle mass, quality and strength which is more common in older adults and has been considered a precursor syndrome or the physical manifestation of frailty. Age-associated changes to the immune system have been suggested as contributors to sarcopenia and frailty but a direct causative role remains to be established. In recent decades life expectancy has increased but healthy life expectancy has not been increased to the same extent, which means people are living more years with a functional loss.
-
Biology of frailty and aging
-
Cognitive frailty
-
Epidemiology
-
Nutrition and Aging
-
Osteoporosis & Frailty
-
Osteoporosis & Sarcopenia
-
Physical exercise
-
Rejuvenation
Track 13: Genetics of Aging
Genetics of aging is generally concerned with life extension associated with genetic alterations, rather than with accelerated aging diseases leading to a reduction in lifespan. Several genetic factors are implicated in aging. A current study of biological aging shows that some aging-associated changes are programmed, whereas others are random and unpredictable
-
DNA repair and Telomeres
-
Genetic and Epigenetic mechanisms
-
Genetic engineering
-
Genetic factors in aging
-
Life extension
-
Mutation
Track 14: Geriatrics
Geriatrics is a special branch of medicine that focuses on health care of elderly people. It promotes health in older adults by preventing and treating diseases and disabilities. People who are growing old are more susceptible to several medical complications such as neurological, respiratory, orthopaedic and cardiovascular diseases. Geriatrics differs from adult medicine because it focuses on the unique needs of the elderly person. Geriatricians focus primarily in the context of multiple chronic conditions, and on preserving function. Elderly patients frequently require an assortment of services with medicinal services and different issues. Geriatric patients sometimes may require home care, which will be given by organizations that utilize nurses and other health care professionals.
-
Clinical geriatrics
-
Genetics of aging
-
Geriatric dentistry
-
Geriatric gastroenterology
-
Geriatric nephrology
-
Geriatric otolaryngology
-
Geriatric rehabilitation
-
Geriatric surgery
-
Stem cells and aging
Track 15: Law and Aging
Law for old aged people is to strengthen and secure the legal rights, dignity, autonomy, quality of life, and quality of care of aging persons. It improves the quality of life for elderly people, including those who are poor or otherwise isolated by lack of education, language, culture, disability or other barriers.
-
Elder abuse
-
Guardianship
-
Health Care Decision Making
-
Neglect & Exploitation
-
Retirement
Track 16: Life Extension Science
Life extension science is the concept of extending the human lifespan, both modestly – thru enhancements in medicine – or dramatically by way of growing the maximum lifespan. The potential to acquire such dramatic modifications, however, does not currently exist. Scientists believe that future breakthroughs in tissue rejuvenation, stem cells, regenerative medicinal drug, molecular repair, gene therapy, pharmaceuticals, and organ replacement (which includes with artificial organs or xenotransplantations) will ultimately allow human beings to have indefinite lifespans via whole rejuvenation to a healthy younger condition.
-
Cloning and Body part replacement
-
Genetic editing
-
Pharmaceutical science
-
Regenerative medicine
-
Rejuvenation
Track 17: Mechanism of Aging
Aging is the process of becoming older. Aging processes involves molecular, biochemical and biological mechanisms. In humans, aging represents the accumulation of changes encompassing physical, psychological, and social changes. For most human diseases aging is among the greatest known risk factors. The process of aging is driven at the cellular level by random molecular damage that accumulates slowly with age. Although cells mechanisms repair or remove damage, they are not fully efficient and their efficiency declines with age. No genes are known to have evolved specifically to cause damage; Aging is not a programmed process. In determining life-span the role of genetics is complex and paradoxical.
-
Aging and Genetic determinants
-
Aging genetic disorders
-
Aging genomics
-
Bioinformatics in aging
-
Epigenetics of aging
Track 18: Nutrition and Healthy Aging
Choosing healthy foods may be a smart thing to achieve the ultimate goal of healthy and active maturing. Malnutrition is increasingly common within the older population. This can be a serious issue since malnutrition can be very terrible for health. Many individuals over the age of 65 are either under- or over-nourished. Among older individuals living in their own homes, almost 1 in 10 are suffering from under-nutrition. Many healthy older adults report that they skip at least one meal a day. For individuals over the age of 65 who become hospitalized, their risk of becoming undernourished may rise to as much as 60%. On the other hand, as much as one-third of individuals over the age of 65 endure from over-nutrition. That’s, they eat too much. The result could be a high rate of overweight and obesity in this age group.
-
Anti-aging foods
-
Changes in bone density
-
Changes in digestion
-
Changes in metabolism
-
Dehydration and Constipation
-
Malnutrition
-
Nutraceuticals
-
Nutrition for older adults
-
Sensory changes
Track 19: Senescence
Senescence is defined as the period when synthetic (anabolic) biochemical process gives way to a degradative (catabolic) process. In general, it is the phenomenon of aging. It is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics. It is the inevitable fate of all multicellular organisms with germ-soma separation, but it can be delayed. The pattern of Senescence can be Cellular Senescence, Tissue Senescence, Organ Senescence, Organism or Whole plant Senescence
-
Acute and Chronic senescence
-
Cellular senescence
-
Immunosenescence
-
Impact of senescence on human health
-
In vitro senescence
-
Therapy-induced senescence
Track 20: Theories of Aging
Theories of aging may be divided into classes: those that answer the query “Why do we age?” then that is an evolutionary theory of aging and those that deal with the question “How do we age?” then it is a physiologic theory of aging. These theories compete with each other, making it not likely that multiple of them could be true. Over time, a few theories have fallen out of favour as others have turn out to be more extensively accepted. Other theories, more properly referred to as hypotheses, are smaller in scope and address the question, “How will we age?” They try to provide an explanation for the mechanisms that affect how we and other species age, and it is possible that a number of them are concurrently true. Checking out these hypotheses is the current pursuit of most aging ¬research. Identification of the mechanisms that affect aging ought to cause interventions that slow or modify aging. Current research means that there may be a limited number of these mechanisms, giving scientists hope that their efforts may additionally one-day cause strategies that would assist us to lead longer, healthier lives.
-
Accumulation theories
-
Antagonistic pleiotropy theory
-
Clinker theories
-
Clunker theory
-
DNA/Genetic Theory
-
Systemic signalling theory
-
Unified theory of aging
MARKET ANALYSIS of Aging Conference
Importance & Scope
Aging Meet 2019 is a unique forum to share and gain knowledge in the field of Aging and Gerontology. The main aim of this conference is to stimulate new ideas for Promoting Healthy Aging.
Aging Meet 2019 mainly aims to bring Global-renowned speakers, Geriatricians, Geriatric Physicians, Doctors, Professors, Social workers, Health care administrators, Geriatric Care Managers, Nurses, Palliative care specialists, Researchers and Students from different geographic regions can share their valuable insights on the advancements in the field of Aging, Geriatrics and Gerontology.
Why Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia?
Kuala Lumpur is vibrant mix and incense-wreathed, colourfully decorated mosques and temples of the country’s Malay, Chinese and Indian communities. Kuala Lumpur is the capital of Malaysia, boasting gleaming skyscrapers, colonial architecture, charming locals, myriad of natural attractions and trendy nightspot. Kuala Lumpur offers a mouth-watering mix of Asian culinary traditions for the food lovers. Malaysia is a favourite destination for many multinational companies. The Malaysian government is dedicated to creating a dynamic and progressive business environment to ensure potential investors are drawn into a thriving economy. An admiration for these ancient cultures is well balanced with a drive to be plugged into the modern world, as evidenced by an exciting contemporary art and design scene and a buzzing digital economy.
Things to do in Malaysia
- Feel on Top of the World at Petronas Twin Towers
- Hit the Casino at Genting Highlands, Pahang
- Relive your Childhood at Legoland and Hello Kitty Town, Johor
- Fulfil your Shopping Ambitions at BBKLCC, Kuala Lumpur
- Foodies Rejoice at Jalan Alor, Kuala Lumpur
- Dive Away to an Underwater Universe at Sipadan Island, Sabah
- Relax with Tea and Scones at Cameron Highlands, Pahang
Overview
Aging is the practice of becoming older. The term Aging refers significantly to Homo sapiens, several animals, and fungi, bacterium and perennial plants. Aging may also be brought up as single cells among associate organism that have ceased dividing (cellular senescence) or to the population of a species (population aging).In humans, aging represents the amassing of changes in a human being over time, including social, psychological and physical changes. Aging is amongst the greatest known risk factors for most human diseases. Roughly one hundred fifty thousand die day after day across the world, about two-thirds die from age-related causes. Gerontology specifically states the study of psychological feature, social, psychological, cultural and biological aspects of aging. It is distinguished from gerontology, the branch of medication that focuses on the treatment of prevailing unwellness in older individuals.
This event can wear down the analysis and method of aging, so-called Gerontology. This field of science majorly focuses on Senescence, Aging Demographics, and social theories of geriatrics, Bio-gerontology, Environmental geriatrics, Life extension science (anti-aging medicine), Experimental geriatrics, and medical speciality geriatrics
Global Analysis
Global gerontology/ aging market is expected to witness a healthy growth over the forecast period owing to significant factors such as increasing geriatric population and constantly improving geriatric care management services infrastructure. Furthermore, growing demand for aging studies and gerontology graduate programs and favourable government initiatives are the major factors contributing to the development of gerontology/aging market. Additionally, the availability of various care homes, adult day care centres, assisted living and nursing homes are one of the critical success factors for the growth of the market over the forecast period. Gerontology has immensely gained importance in educational institutions, healthcare centres and research institutes investigating the multidisciplinary aspects associated with the geriatric population.
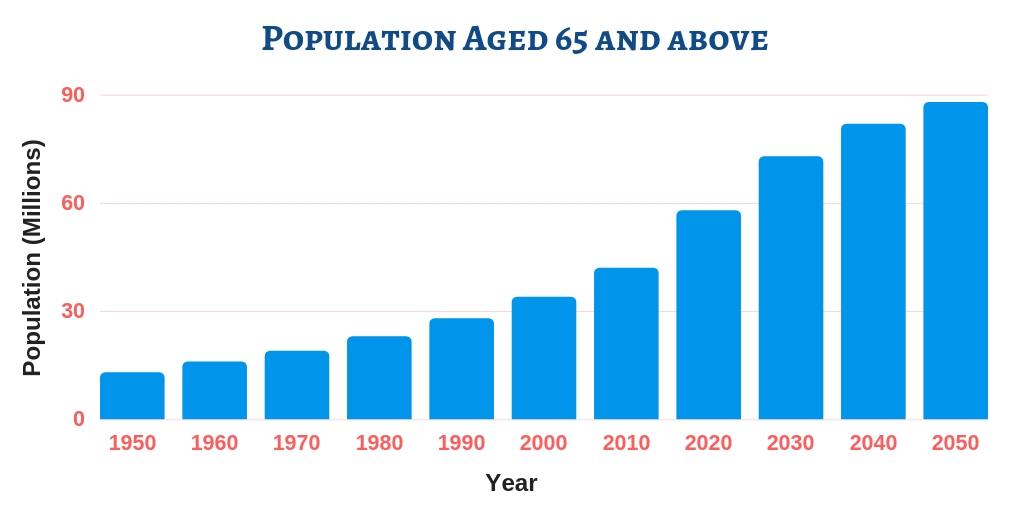
Regional Analysis
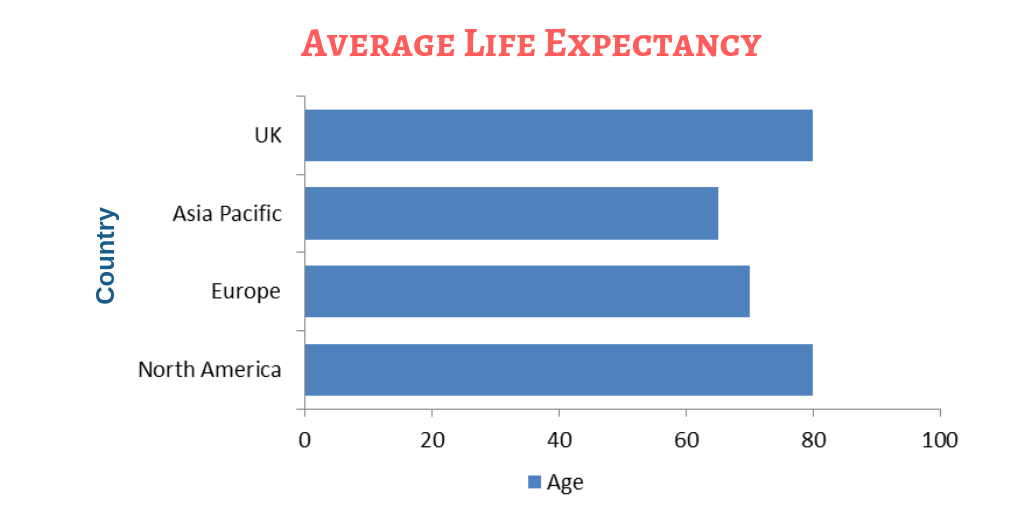
Geographically, North America accounts for one of the largest markets followed by Europe. Baby boomers play a major role in market growth. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the average life expectancy in the U.S. will be 77.1 years for men and 81.9 years for women by 2020. To tackle the rising aging population, favourable reimbursement policies and extensive presence of care centres are set up to assist the problems faced by aged people. Asia Pacific is anticipated to be the fastest growing region due to the factors such as the rise in persistent medical conditions and rising concern for life expectancies among the geriatric population. Latin America holds a strong potential for the market growth owing to the high presence of geriatric population and growing health care facility.
Target Audience
-
Geriatricians
-
Physicians
-
Geriatric Physicians
-
Medical Directors
-
Dental Professionals
-
Geriatric Doctors
-
Ophthalmologists
-
Rheumatologists
-
Clinical Geriatrics
-
Geriatric Nurses
-
Pulmonologists
-
Pharmacists
-
Geriatric Specialist
-
Occupational Therapists
-
Healthcare Faculty
-
Social Workers
-
Community care coordinators
-
Palliative care specialists
-
Students and others interested in the field of Geriatrics
· 
New therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease
Researchers have identified a novel mechanism and potential new therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Alzheimer's is characterized by profound memory loss and synaptic failure. Although the exact cause of Alzheimer's remains unclear, it is well established that maintaining memory and synaptic plasticity requires protein synthesis.
Researchers recently have shown AD-associated activation of a signalling molecule termed eEF2K leads to inhibition of protein synthesis. In this study, they wanted to determine if suppression of eEF2K could improve protein synthesis capacity and consequently alleviate the cognitive and synaptic impairments associated with the disease.
The researchers used a genetic approach to repress the activity of eEF2K in two different Alzheimer's mouse models. They found that genetic suppression of eEF2K prevented memory loss in those animal models and significantly improved synaptic function.
Can existing antidepressant slow down Alziemer's?!
Old age could become more bearable for millions of people if an existing antidepressant is found to fulfil its potential in the battle against Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Scientists believe that trazodone could slow down the progression of neurodegenerative conditions.
Researcher says it could work by accelerating the rate of production of proteins that protect against brain cell death.
Brain cell degeneration occurs when cells become stressed, which leads to them not producing enough protein. This, in turn, prevents them from working properly and the eventual death of the cell. It is a common factor in a number of conditions, from Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s to CJD.
There is currently no cure for dementia and scientists are not suggesting that trazodone would be one either. It would not prevent the onset of the condition but could be used to slow its progression. This could greatly improve the quality of life for people diagnosed with dementia and allow them to live independently for longer.
Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia, representing between 60 per cent and 70 per cent of diagnoses. It particularly affects those aged 65 and older, slowly destroying memory and making it difficult to carry out everyday tasks.
Early diagnosis is important so that as much memory can be preserved as possible. If you have elderly relatives, then it’s worth keeping an eye out for common symptoms. These include problems remembering newly learned information and disorientation.
Raising concerns with medical professionals will mean they can conduct tests to get a definitive diagnosis. There’s lots of support available for both those with dementia and people who care for people with the condition. Alzheimer’s progresses over time, moving from the early stages when they can function relatively independently until they rely on others for nearly everything.
Conference Highlights
- Aging and Gerontology
- Aging and Mental Health
- Aging and Technology
- Aging Care Management
- Aging Disorders
- Anti-Aging Strategies
- Antioxidants and Aging
- Cultural Diversity in Aging
- Economic and Social Impact of Aging
- Evolution of Aging
- Frailty/Sarcopenia
- Genetics of Aging
- Geriatrics
- Law and Aging
- Life Extension Science
- Mechanisms of Aging
- Nutrition and Healthy Aging
- Senescence
- Theories of Aging
- Aesthetic Medicine
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | April 22-23, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Aging Science
- Journal of Gerontology & Geriatric Research
- Journal of Aging and Geriatric Medicine
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by


























